Implementing GitOps Preview Environments with ArgoCD on EKS
Introduction
As our applications grew and our development teams expanded, we needed a reliable way to preview code changes before merging them into production. Traditional preview deployments worked well initially, but we wanted a solution that aligned with our GitOps workflow and could scale seamlessly within our AWS EKS infrastructure.
That's when we implemented GitOps-based preview environments with ArgoCD. This setup allows each pull request to automatically spin up its own isolated environment on Kubernetes, complete with an ingress domain that includes the PR number as a subdomain. Whenever a PR receives new commits, the corresponding environment automatically updates with the latest image tag. Once the PR is closed or merged, the environment is automatically cleaned up—saving costs and reducing manual overhead.
In this post, we'll walk through how we set up preview deployments using ArgoCD on EKS, the challenges we faced, and how this approach improved our deployment speed, consistency, and developer experience.
How It Works
The following diagram illustrates how our GitOps-based preview environment workflow is structured with GitHub Actions, ArgoCD, and AWS EKS.
ArgoCD Preview Deployment Architecture
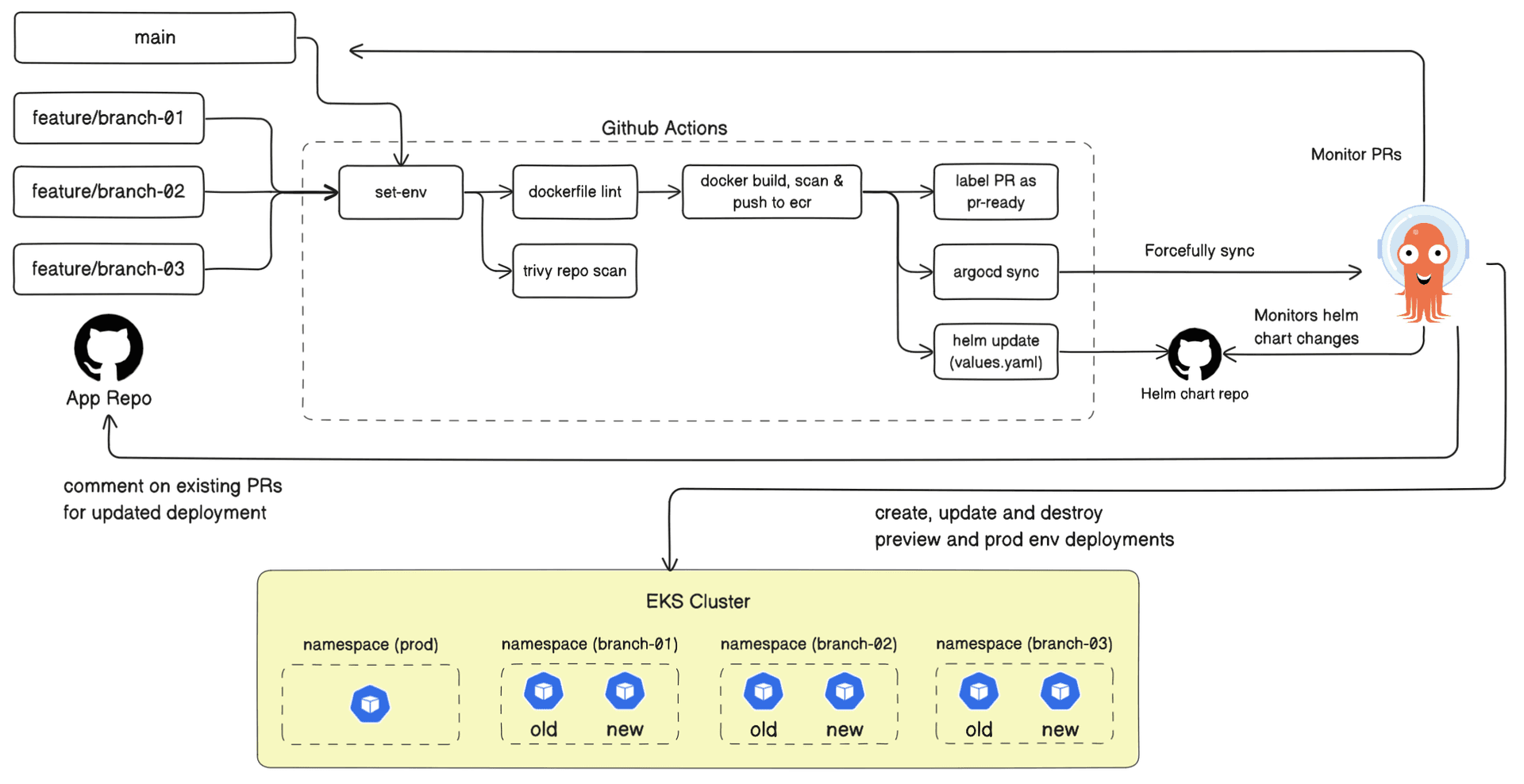
Each pull request triggers a dedicated CI/CD pipeline in GitHub Actions, which performs a series of automated steps:
- Environment setup: Detects the deployment environment by checking the branch type and defines environment variables such as the PR number and branch name
- Static checks: Runs Dockerfile linting and vulnerability scanning using Trivy
- Image build and push: Builds the Docker image, tags it with the environment name and commit SHA, and pushes it to Amazon ECR
- Helm chart update: Updates the
values.yamlfile with the new image tag (only for production deployments) - Label PR: Labels the PR as "preview-ready"
- ArgoCD sync: Manually calls the ArgoCD sync API to deploy the updated Helm chart
ArgoCD continuously monitors both the application repository and the Helm chart repository for changes. When a new or updated PR is detected, it automatically syncs the configuration and deploys the corresponding environment into a dedicated namespace within the EKS cluster.
Each namespace is named after the branch or PR number (for example, branch-01 and appname-pr-123), ensuring isolation between environments. Once a PR is closed or merged, the corresponding namespace is deleted.
Prerequisites: This guide assumes you already have a running Kubernetes cluster with ArgoCD installed and your application repository includes a Helm chart.
Create ArgoCD ApplicationSet
The ApplicationSet is at the core of how preview environments are dynamically created and destroyed. It allows ArgoCD to automatically generate ArgoCD Application resources based on a defined generator—in our case, pull requests from GitHub.
Whenever a new pull request is opened, the ApplicationSet controller detects it through the PR generator and automatically creates a new ArgoCD Application pointing to the corresponding branch or commit. Each application deploys into its own namespace, typically named after the PR number or branch name.
First, we need to create a GitHub token secret, which will be used by ArgoCD to call the GitHub API to detect opened pull requests.
k create secret generic github-token \ --from-literal=token=<GITHUB_PERSON_ACCESS_TOKEN>bash
We're providing the Helm values as a string in the ApplicationSet itself because this is a Next.js frontend application and we only need to override basic settings like name, fullname, image tag, and ingress host.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: ApplicationSet metadata: name: app-preview-deployment namespace: argocd spec: goTemplate: true goTemplateOptions: ["missingkey=error"] generators: - pullRequest: github: owner: nik repo: app-repo tokenRef: secretName: github-token key: token labels: - preview-ready # Triggers only when PR is labeled as preview-ready requeueAfterSeconds: 60 template: metadata: name: 'app-ui-pr-{{ .number }}' namespace: argocd annotations: notifications.argoproj.io/subscribe.sync-operation-change.github: nik-argocd-preview-deployment notifications.argoproj.io/github.repo: "nik/app-repo" argocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.number: "{{ .number }}" argocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.head_sha: "{{ .head_sha }}" spec: project: default source: repoURL: https://github.com/nik/app-helm-chart.git targetRevision: main path: helm-chart helm: valueFiles: - values.yaml values: | nameOverride: app-ui-pr-{{ .number }} fullnameOverride: app-ui-pr-{{ .number }} serviceAccount: create: true name: "app-ui-pr-{{ .number }}-svc-acc" image: repository: "1234567.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/internal/app-repo" tag: preview-{{ .head_short_sha_7 }} ingress: hosts: - host: app-ui-pr-{{ .number }}.awsp.nik.xyz paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix tls: - hosts: - app-ui-pr-{{ .number }}.awsp.nik.xyz secretName: app-ui-pr-{{ .number }}-awsp-domain-tls destination: server: https://kubernetes.default.svc namespace: app-ui-pr-{{ .number }} syncPolicy: automated: prune: true selfHeal: true managedNamespaceMetadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/instance: app-ui-pr-{{ .number }} annotations: argocd.argoproj.io/tracking-id: >- app-ui-pr-{{ .number }}:app/Namespace:app-ui-pr-{{ .number }}/app-ui-pr-{{ .number }} syncOptions: - CreateNamespace=trueyaml
Create GitHub Actions Workflows
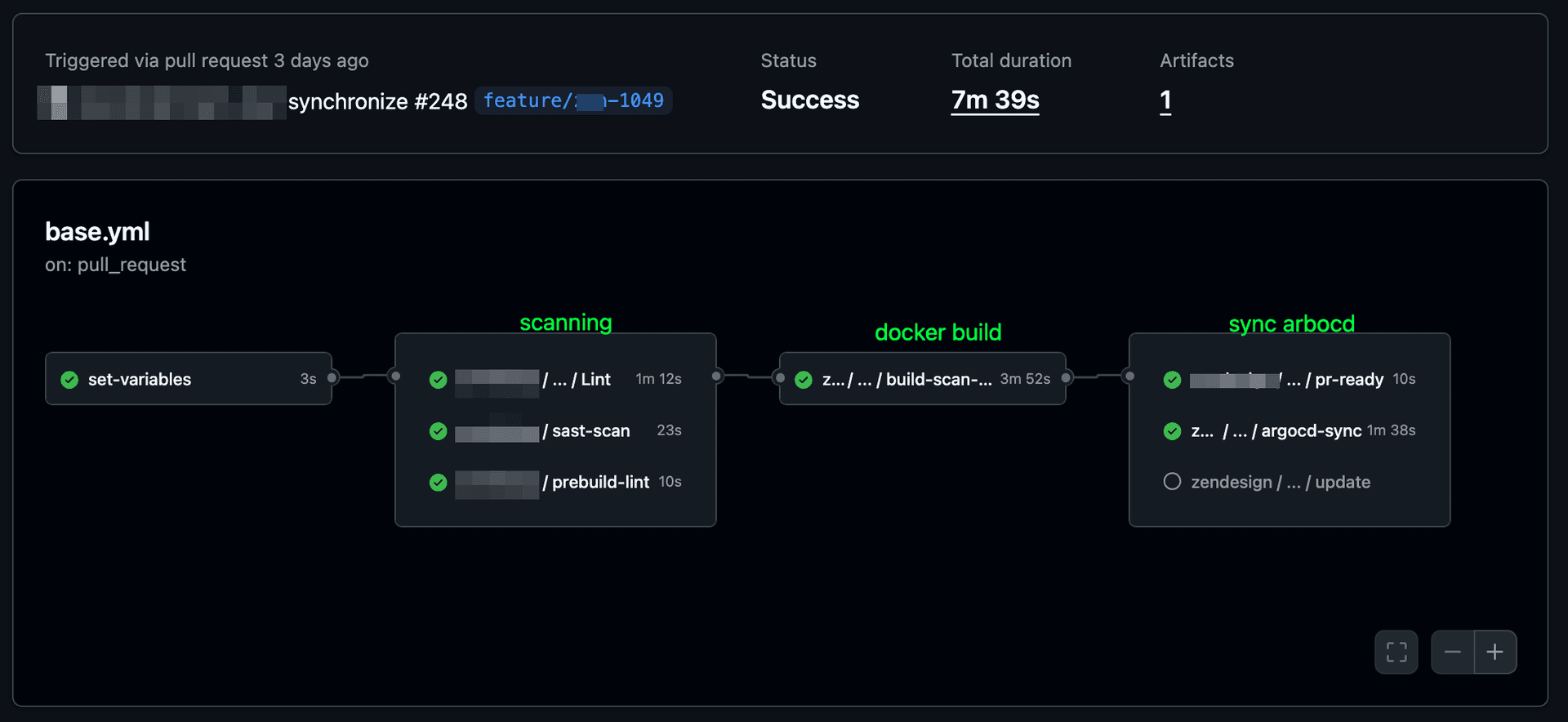
Detect the Deployment Environment
set-variables: runs-on: ubuntu-latest outputs: deploy-env: ${{ steps.set-env.outputs.deploy-env }} steps: - name: Set deploy environment id: set-env run: | echo "GITHUB_REF is: $GITHUB_REF" BRANCH_NAME="${GITHUB_REF##*/}" if [ "$BRANCH_NAME" == "main" ]; then DEPLOY_ENV="production" else DEPLOY_ENV="preview" fi echo "deploy-env=$DEPLOY_ENV" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUTyaml
Here we're checking which branch the commit lies on. If it's the main branch, we consider it a production deployment (Helm update directly, no PR environment). Otherwise, we consider it a preview deployment. For multiple environments like PR, dev, staging, QA, and prod, we can also refine the existing job to check for specific branch formats.
Docker Build, Trivy Scan, and Push
This job handles the complete container lifecycle:
build-scan-push: environment: ${{ inputs.deploy-env }} outputs: image-tag: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }} runs-on: ${{ inputs.runs-on }} steps: - name: Checkout repository uses: actions/checkout@v3 - name: Get short SHA id: short_sha run: echo "sha_short=$(echo ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha || github.sha }} | cut -c1-7)" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT - name: Docker meta id: meta uses: docker/metadata-action@v5 with: images: ${{ inputs.docker-registry }}/${{ inputs.docker-repository }}/${{ inputs.docker-image-name }} tags: ${{ inputs.deploy-env }}-${{ steps.short_sha.outputs.sha_short }} - name: Configure AWS credentials if: inputs.docker-registry-type == 'ecr' uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4 with: role-to-assume: ${{ inputs.role-to-assume }} aws-region: ${{ inputs.aws-region }} - name: Login to Amazon ECR if: inputs.docker-registry-type == 'ecr' uses: aws-actions/amazon-ecr-login@v1 - name: Build and push image run: | docker build -t ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }} . docker push ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }} - name: Upload Trivy SBOM uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4 with: name: ${{ inputs.project }}-image-sbom path: '${{ github.workspace }}/${{ inputs.project }}-image.sbom.json' retention-days: 1yaml
This job extracts the short SHA hash from the commit, logs into AWS ECR, builds the Docker image, publishes it to our ECR repository, and runs a Trivy scan to generate an SBOM and create a GitHub artifact.
Label the PR as Preview-Ready
This is a very important step. Our ArgoCD is monitoring the repository PRs, but it's not taking any action until there is a preview-ready label on that PR.
pr-ready: needs: build-scan-push if: inputs.deploy-env == 'preview' runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout (for GitHub CLI) uses: actions/checkout@v4 - name: Add 'preview-ready' label to PR env: GH_TOKEN: ${{ github.token }} PR_NUMBER: ${{ github.event.number }} run: | gh pr edit "$PR_NUMBER" --add-label "preview-ready"yaml
You might be thinking, "Why are we doing this? Can't we just monitor PRs only?" The reason is that in our case, it takes ~5-8 minutes to build the Docker image. If we trigger ArgoCD based on the PR event, ArgoCD will deploy the application but it will fail with an ImagePullError because the Docker build isn't completed yet and there's no image on ECR for that commit. To avoid this issue, we label our PR only after the Docker build and push job is successful.
ArgoCD Trigger
Once the PR is labeled as preview-ready, our ArgoCD will consider that PR and the ApplicationSet will do its magic—creating an ArgoCD app with the Helm chart deployment.
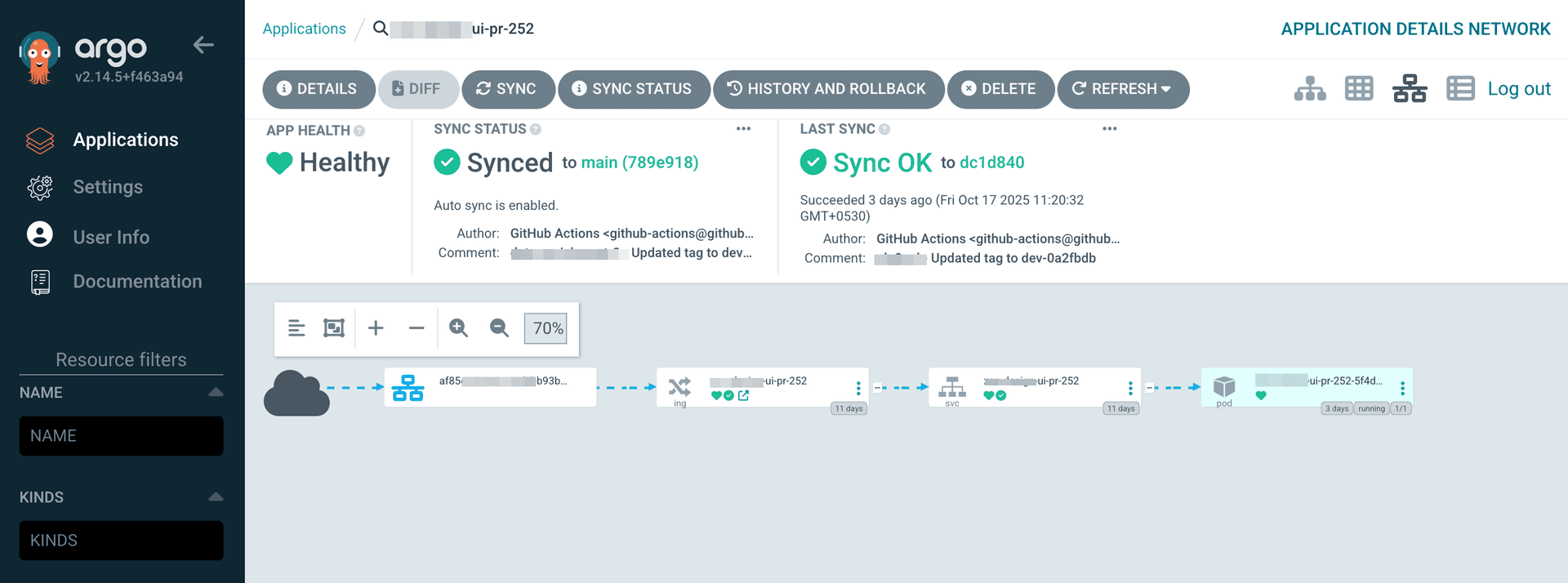
As we can see, our application is up and running in an isolated namespace.
Updating Existing PR
Now let's say a developer wants to push hotfixes to an existing PR and we want to deploy them into the existing environment that we created for that PR. It's very straightforward—our ArgoCD app is already monitoring the PR, so if we push any commit to that PR, ArgoCD will detect it and try to sync it. However, it won't be able to pull the updated Docker image (our previous ImagePullBackOff error) because it's still in the build process. That's fine in this case because the PR is already labeled as preview-ready, so once the Docker image is built, we will forcefully sync the ArgoCD app. This time we're 100% sure that ArgoCD will be able to pull the image because our Docker build stage was completed.
argocd-sync: if: inputs.deploy-env == 'preview' environment: ${{ inputs.deploy-env }} runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout code uses: actions/checkout@v4 - name: Install ArgoCD CLI run: | curl -sSL -o argocd-linux-amd64 https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/latest/download/argocd-linux-amd64 sudo install -m 555 argocd-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/argocd rm argocd-linux-amd64 - name: Set ArgoCD app name run: | APP_NAME="${{ inputs.argocd-app-name }}-${{ github.event.number }}" echo "ARGOCD_APP_NAME=$APP_NAME" >> $GITHUB_ENV - name: Login to ArgoCD run: | argocd login ${{ secrets.ARGOCD_SERVER }} \ --username ${{ secrets.ARGOCD_USERNAME }} \ --password ${{ secrets.ARGOCD_PASSWORD }} \ --insecure - name: Sync ArgoCD Application run: | argocd app sync $ARGOCD_APP_NAME --force argocd app wait $ARGOCD_APP_NAME --timeout 600 --healthyaml
Adding Comments in PR
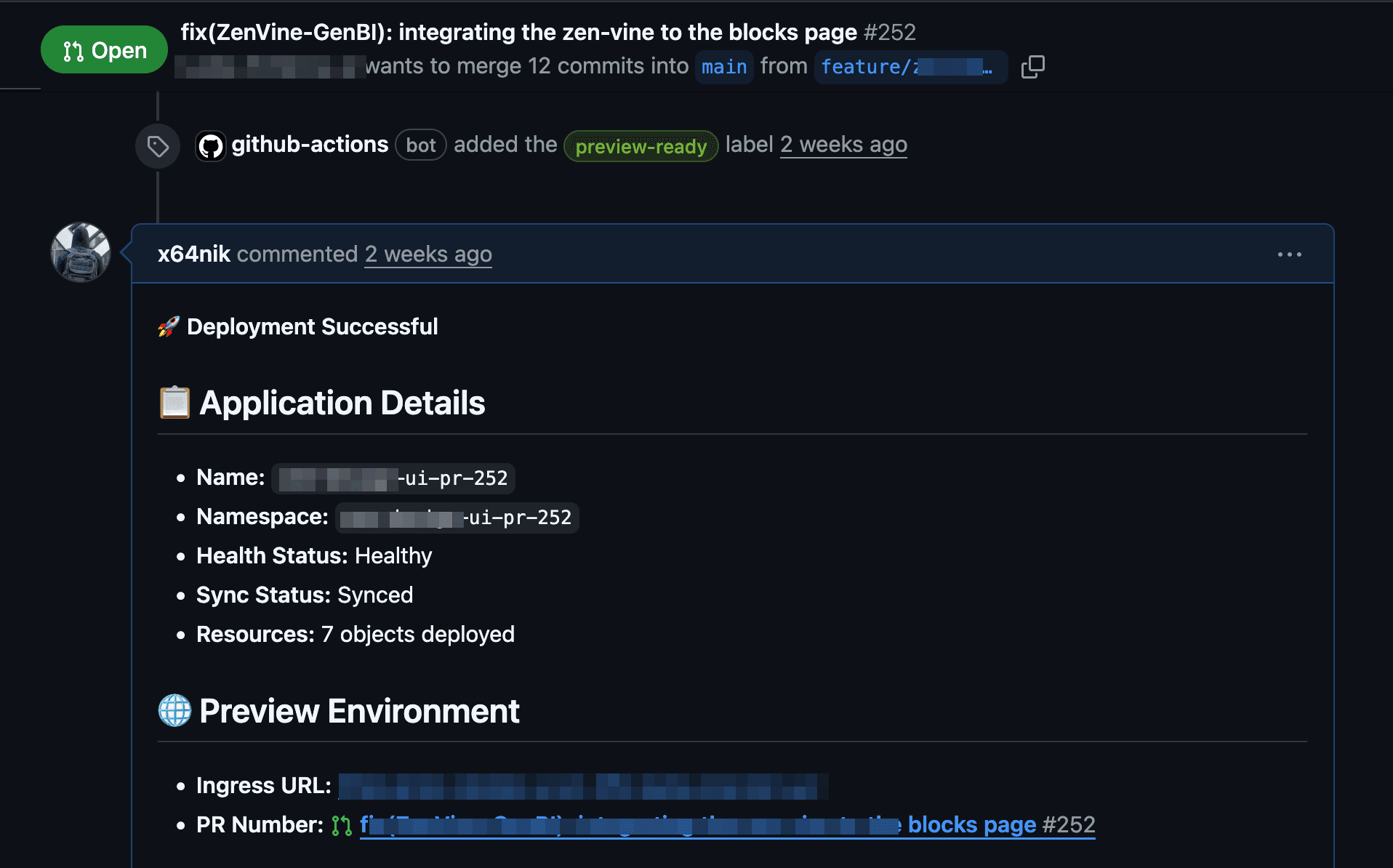
Once the PR is successfully deployed to the preview environment, we wanted developers to receive instant feedback directly in the PR itself — without needing to open ArgoCD. To achieve this, we configured ArgoCD Notifications to post a detailed deployment comment in the corresponding GitHub PR whenever the application reaches a healthy state.
Using a ConfigMap (argocd-notifications-cm), we defined a GitHub webhook service and a trigger that listens for sync and health status changes in ArgoCD applications. When the status becomes Healthy, ArgoCD automatically sends a webhook request to the GitHub API, adding a formatted comment to the PR.
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: argocd-notifications-cm namespace: argocd data: service.webhook.github: | url: https://api.github.com headers: - name: Authorization value: token $github-token - name: Accept value: application/vnd.github.v3+json trigger.sync-operation-change: | - when: app.status.health.status == 'Healthy' send: [github-pr-comment] template.github-pr-comment: | webhook: github: method: POST path: /repos/{{index .app.metadata.annotations "notifications.argoproj.io/github.repo"}}/issues/{{index .app.metadata.annotations "argocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.number"}}/comments body: | { "body": "🚀 **Deployment Successful**\n\n## 📋 Application Details\n- **Name:** `{{.app.metadata.name}}`\n- **Namespace:** `{{.app.spec.destination.namespace}}`\n- **Health Status:** {{.app.status.health.status}}\n- **Sync Status:** {{.app.status.sync.status}}\n- **Resources:** {{.app.status.resources | len}} objects deployed\n\n## 🌐 Preview Environment\n- **Ingress URL:** [https://app-ui-pr-{{index .app.metadata.annotations "argocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.number"}}.domain.xyz](https://app-ui-pr-{{index .app.metadata.annotations "argocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.number"}}.domain.xyz)\n---\n*🤖 Automated deployment notification from ArgoCD*" }yaml
Here we're using the GitHub personal access token that we generated previously to call the GitHub API.
annotations: notifications.argoproj.io/subscribe.sync-operation-change.github: oraczen-argocd-preview-deployment # This is what the notification template will use for repoURLPath notifications.argoproj.io/github.repo: "nik/app" # Additional context for notifications argocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.number: "{{ .number }}" argocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.head_sha: "{{ .head_sha }}"yaml
These annotations are added to each ArgoCD Application so that the notification system knows which pull request and repository to interact with.
notifications.argoproj.io/subscribe.sync-operation-change.github— subscribes the application to the GitHub notification trigger, ensuring a comment is added when the sync operation status changesnotifications.argoproj.io/github.repo— specifies the target GitHub repository where the pull request existsargocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.number— dynamically references the PR number, allowing ArgoCD to comment on the correct pull requestargocd-notifications.argoproj.io/github.pr.head_sha— captures the PR's latest commit SHA, which can be useful for tracking which commit was deployed in the preview environment
In short, these annotations bridge the connection between ArgoCD and GitHub, enabling automated, PR-specific deployment notifications.
Conclusion
Implementing GitOps-based preview environments with ArgoCD on EKS has significantly streamlined our development and review process. Every pull request now automatically gets its own isolated environment, giving developers and reviewers instant access to a live version of the changes before merging. This not only improves collaboration and testing accuracy but also reduces manual deployment overhead.
By leveraging ArgoCD's ApplicationSet, Notifications, and GitHub integration, we achieved a fully automated workflow—from PR creation to deployment and cleanup. It aligns perfectly with GitOps principles, ensuring that every environment is declarative, traceable, and reproducible.
Overall, this setup has enhanced visibility, consistency, and speed across our CI/CD pipeline. It's a scalable foundation that we can continue to build on as our infrastructure and teams grow.